|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Dice Alternatives and Substitutes Dice are the most obvious and common of all randomizing objects but there are a number of other related objects, shapes and devices that can be used for generating random results for social games and related activities like gambling, divining, fortune telling, prediction, etc. Before dice became commonly available they were preceded by a number of other methods for generating unpredictable results for social games and divination. Learn about dice's ancestors and mankind's other ingenious ideas on how to come up with a random result that is not consciously predetermined by anyone or anything other than the natural forces of nature. Two Faced Flat Shapes The original randomizing objects used by ancient peoples dating from pre-history were sets of two-sided flat sticks, flat sea-shells, nut-shells, pebbles, etc, used by witch doctors and shaman to give omens, receive messages from the gods, and to tell of things to come.
Many tribes all over Africa have witch doctors who use spotted flat sticks (known as dollasses), made of wood or ivory, as dice for divination and fortune telling
. Bones Animal bones were commonly used as dice in ancient times and are still used by some Native-American and Mongolian tribes to this day. The Egyptians, Romans and Greeks threw knucklebones and anklebones as dice, for divining, gambling and social games. The Roman name for these was Astragalus's and many examples of Astragulus gaming objects can often be found in Roman and Greek archaeological excavation sites. In fact, these anklebones are found considerably more often than any other type of bone in ancient sites of human activity.
The earliest known reference to an Astragalus is found in an Egyptian painting illustrating a nobleman and his wife gambling with an Astragalus in some kind of board game. The painting is dated to around 3500 BC and it can be safely assumed that bones as dice were used by ancient people from much earlier in history.
Rolling Logs
An extremely ancient relative to dice is the
rolling log. These are long barrel-like objects which are rolled
along and come to a standstill with a particular random
Other similar modern rolling objects like the Anti-Prism shapes below can be readily purchased. They are anti-prisms in shape but with tapered ends so they can only ever come to rest on a uniform triangular shaped face. (For more on Anti-Prisms see polyhedral dice geometry.)
Spinners, Teetotums and Dreidels Another common method of generating random results is to use a spinning-top type object (sometimes known as Teetotums). These are barrel-like shaped objects with a centrally aligned protruding point which are spun like spinning tops so that they will come to rest with one side randomly facing up to indicate the result. Dreidels are four-faced spinners used for a very old traditional Jewish game often associated with and played on the annual Jewish religious celebratory holiday, Hanukkah. The Yiddish word dreydl comes from dreyen ("to turn").
After lighting the Hanukkah menorah, the custom in many Jewish homes is to play the dreidel game. Each player starts the game with 10 to 15 units (coins, chocolates, nuts, raisins, etc), and puts one unit in the "pot". Each player in turn then spins the dreidel, and depending on which side of the dreidel falls face up, either takes from or puts into the pot. The actions of the game (based on a Yiddish version) are as follows:
Another version differs:
The game may continue until the last person has won everything.
The
game of Put & Take is believed to have been developed during the First World War (1914 -
1918) by a soldier in the trenches.
The original spinner was said to have been made from a brass bullet that
was shaped
into a six-sided spinning top.
Each of the six faces had an instruction marked on it as follows: Put One, Put
Two, Put All,
Take One, Take Two, and Take All. Players would ante into a pot and
then take turns spinning the top and depending on the spinner's resulting
instruction
either put in or took from the pot. It was probably originally
played for cigarettes in the trenches. From here the game spread and became
a very popular gambling game during the 1920s and 1930s. It was
greatly played in the North of England in pubs and Working Men's clubs and
was also played to a lesser extent in many other countries. It has
since lost much of its popularity and the mass manufacture of the Put &
Take spinners gradually dwindled. There are many different Put &
Take spinners around, some with a greater number of faces and
instructions, but all are played in much the same way. There were
even crooked spinning tops manufactured that would favour some results
more than others. Ball Shaped Dice Alternatives
Other Randomizing Devices There are quite a few other interesting randomizing devices that have been commercially manufactured. Here are some of them below.
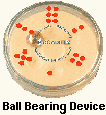
These ball bearing rolling randomizing devices aren't that uncommon. A number of manufacturers have produced devices along these lines. For more examples of these devices see Arjan Verwiej's link below.
There are a number of electronic dice with LEDs (Light Emitting Diodes) that light up randomly when operated. The process of generating random numbers electronically is an interesting topic which deserves a page, explaining its principles, all of its own. Maybe in the future. If you want to learn more on how computers generate pseudo-random numbers see randomly.net. For more electronic dice take a look at Arjan Verwiej's site - Arjan's Electric Dice. For some other very interesting randomizers take a look at Arjan's page - Arjan's Randomizing Devices.
Now learn about Standard Dice or Cubic Dice Without Spots
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Copyright © 2022 Stormdark I.P. and Media. All rights reserved.
www.dice-play.com This site is for
personal use only and content may not be copied or reproduced in any form for any
purpose. Terms &
Conditions
Advertising
UK sports betting sites not on gamstop
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Technically any two-faced flat shape, like
an ordinary coin, is a kind of
dice. It is a two-faced object that can be tossed or thrown to randomly generate
one of two possible results. You could even use a number of coins to
generate greater random numbers.
Technically any two-faced flat shape, like
an ordinary coin, is a kind of
dice. It is a two-faced object that can be tossed or thrown to randomly generate
one of two possible results. You could even use a number of coins to
generate greater random numbers. 
 An Astragalus only
has four sides that it can rest on to indicate its upper face. The
Romans assigned their four-sided anklebone dice the values 1, 2, 3, 6.
The larger 1 and 6 faces had a probability of occurring of about 40% each,
while the smaller 2 and 3 faces only had a probability of around 10%.
An Astragalus only
has four sides that it can rest on to indicate its upper face. The
Romans assigned their four-sided anklebone dice the values 1, 2, 3, 6.
The larger 1 and 6 faces had a probability of occurring of about 40% each,
while the smaller 2 and 3 faces only had a probability of around 10%. result facing up.
There is a very ancient Korean game called Dignitaries that uses
rolling logs like this for random results and many other cultures around
the world have used similar rolling log objects in the same way.
They are one of the few methods of producing dice-like objects with an odd
number of faces. Like Prisms and Anti-Prisms (see
result facing up.
There is a very ancient Korean game called Dignitaries that uses
rolling logs like this for random results and many other cultures around
the world have used similar rolling log objects in the same way.
They are one of the few methods of producing dice-like objects with an odd
number of faces. Like Prisms and Anti-Prisms (see
 Recently there have been some modern versions of
rolling logs commercially manufactured for contemporary games. On the right is a
plastic rolling log for a modern cricket-like game.
Recently there have been some modern versions of
rolling logs commercially manufactured for contemporary games. On the right is a
plastic rolling log for a modern cricket-like game. 
 Each face
of a dreidel bears a letter of the Hebrew alphabet which are named:
Nun,
Each face
of a dreidel bears a letter of the Hebrew alphabet which are named:
Nun,